- Get started
- About
- First steps
- Glossary
- Migration
- Configuration
- Global configuration
- Repository
- Template configuration
- Template scope
- Manage templates
- Supported fields
- Permissions
- Using templates
- Create issue from template
- Create issue structures
- Apply template to existing issue
- Recreate issue
- Use template custom field on issue create screen
- Default templates
- Direct link
- JQL searchers
- Variables
- Static variables
- Dynamic variables
- Smart defaults
- Basics
- Smart issues
- Smart users
- Smart dates
- Smart project
- How to use smart defaults
- App Integrations
- Team-managed projects
- Jira Software
- Jira Service Management
- Advanced Roadmaps
- Issue Checklist for Jira
- Advanced
- Automation
- Legacy automation action
- REST API
- Create issue and apply template with Jira REST API
- Security
- Security statement
- App permissions
How to use smart defaults
The smart defaults feature is a very powerful tool provided by Issue Templates Cloud. In this chapter you can find examples showing how to use smart defaults in your project.
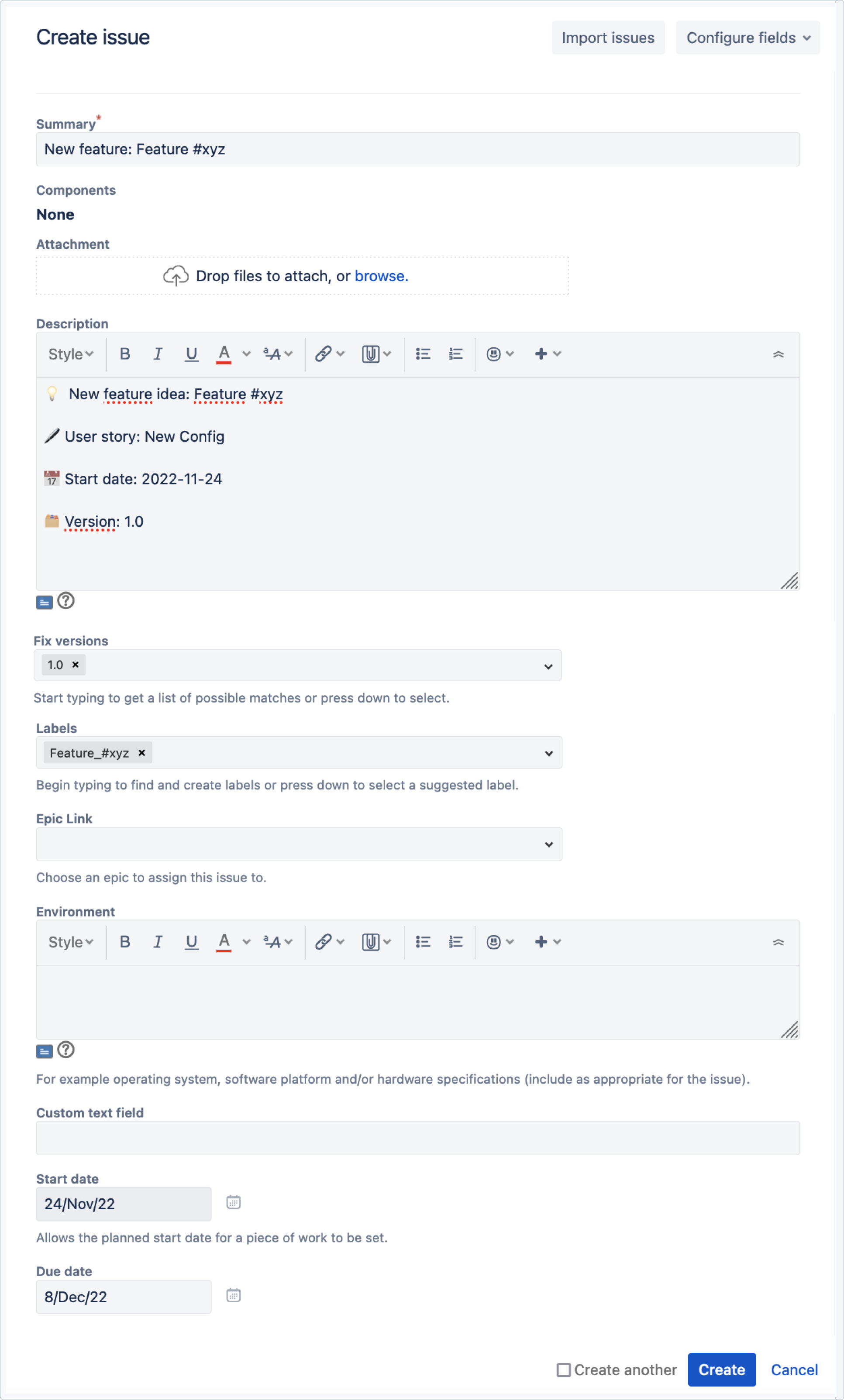
Use case 1 - Implementing a new feature
In this scenario, a user wants to have a template that would automate the process of implementing a new feature. With smart defaults, the process can automate:
- filling the starting date
- setting a deadline
- setting a reporter and assigning an issue to a specific role or person
- creating a label for this feature
- setting a version
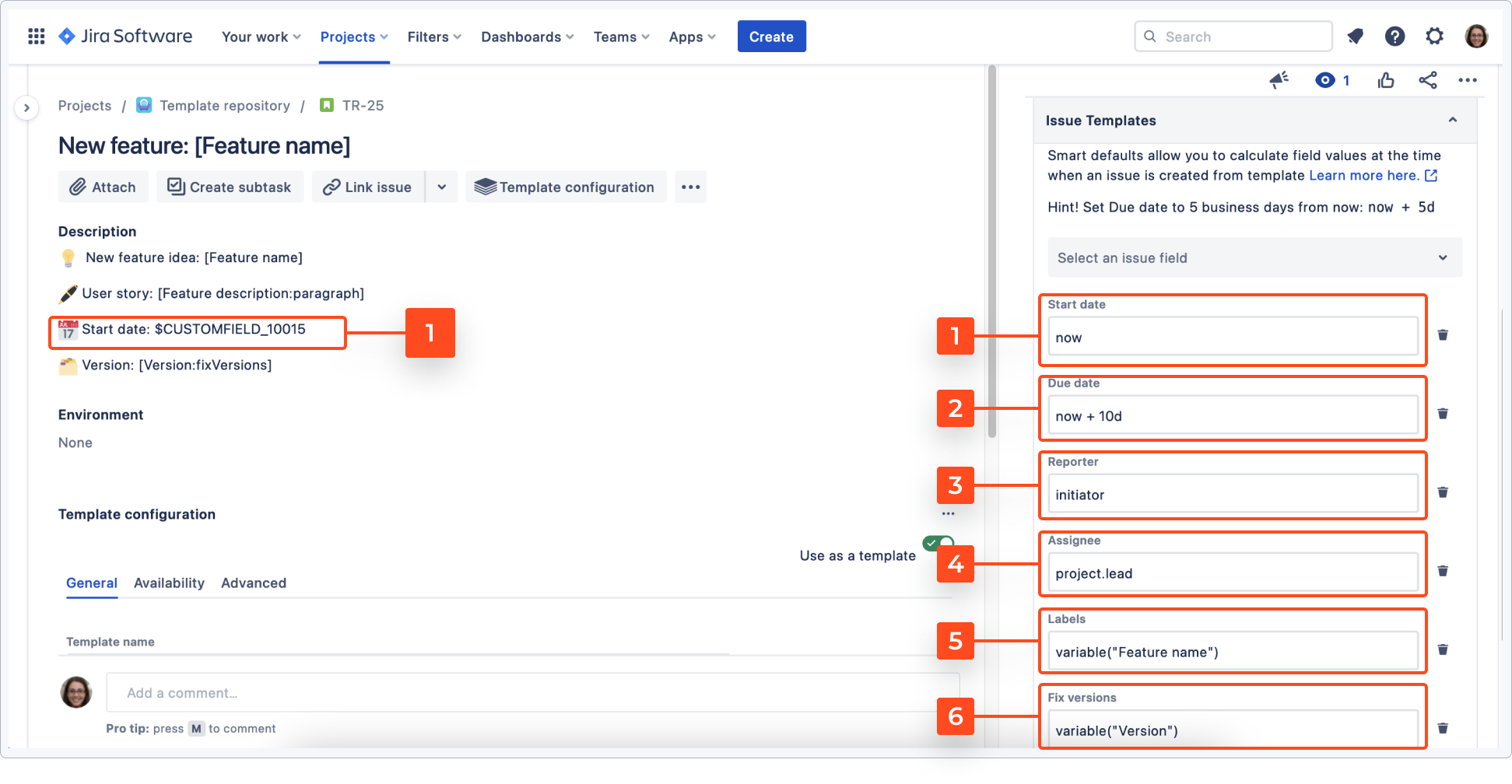
In this case, smart defaults are configured as follows:
- Start date - set to now, so it will automatically fill the start date as the day it was created. Thanks to smart defaults and static variables, this date will be automatically added to the custom field and description. In this case it corresponds with a custom field #10015, but it can be any custom field of a date picker type.
Tip
See Atlassian support for details on checking the ID of a custom field.
- Due date will set a deadline for the process. In this case, it will add 10 business days to the start date using smart dates .
- A person who creates an issue will be assigned as a reporter.
- The issue will be assigned to a specific role, in this case the project lead.
- A label will be automatically created that corresponds with the name of the feature. The label refers to the value you have set in the dynamic variable.
- You can set the version here. The fix version field is based on the value set as the dynamic variable.
The feature name will be automatically applied to the referred fields, such as the summary, new feature idea in the description and the label in this case.
Once the template is configured, the user can navigate to the create from template option to use it.
You will be asked to fill in the feature name, description (user story), and the version.
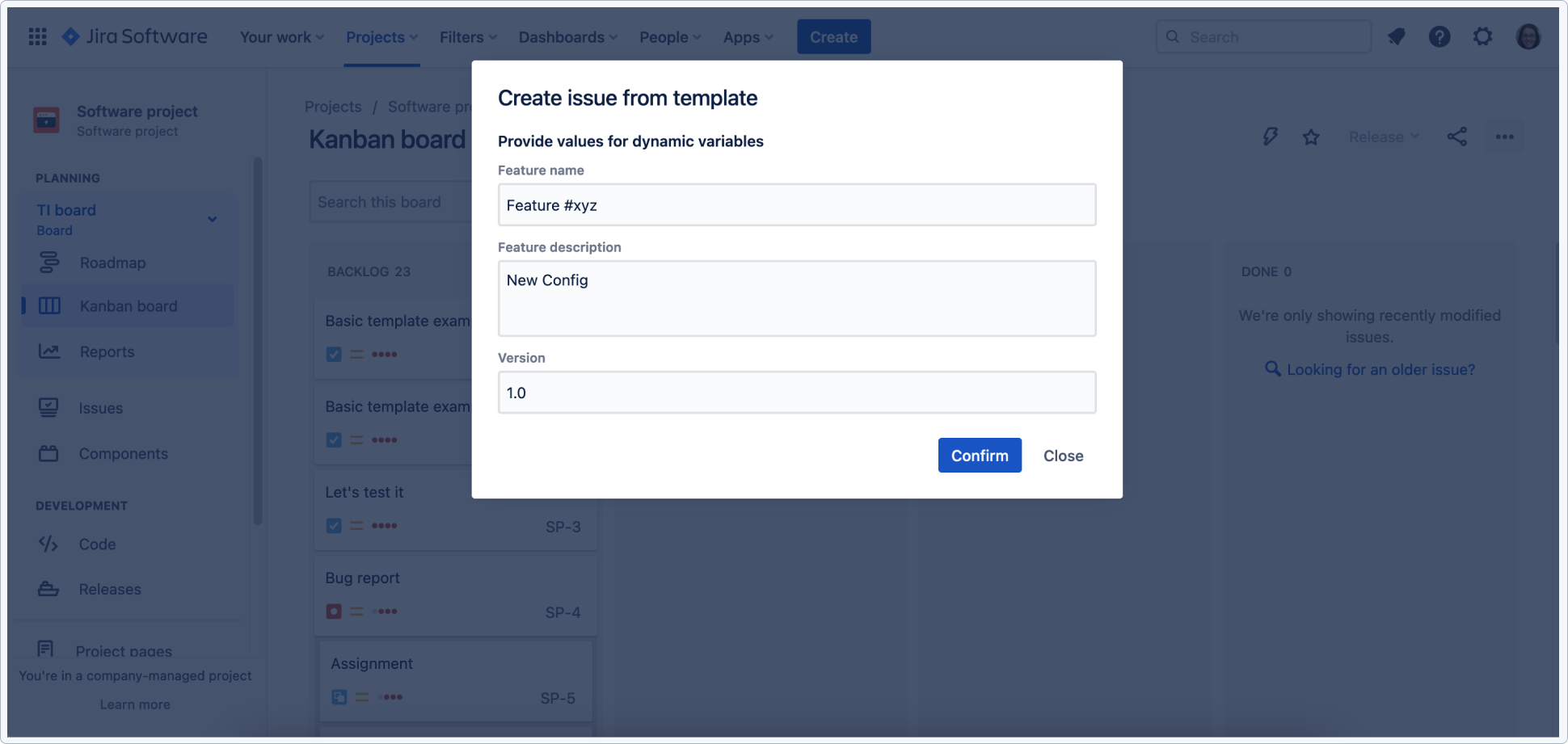
Result
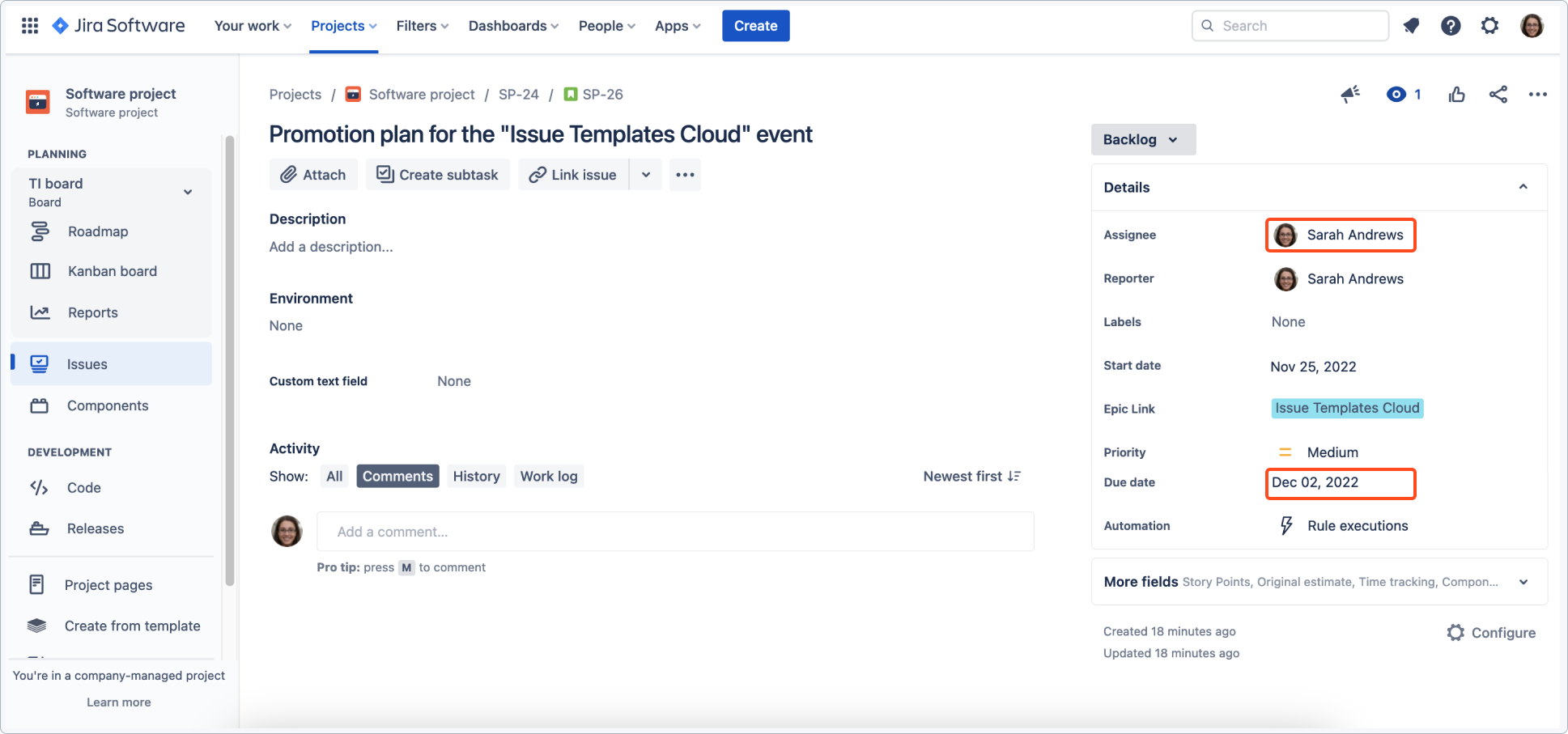
Use case 2 - Preparing a timeline for a complex task with multiple steps
In this scenario, a user wants to plan an event and add steps in form of a timeline. With smart defaults you can offset dates easily, as well as copy values from parent and linked issues. An epic is created that corresponds with planning steps. Steps are added as stories and an epic for a corresponding process that happens simultaneously is linked.
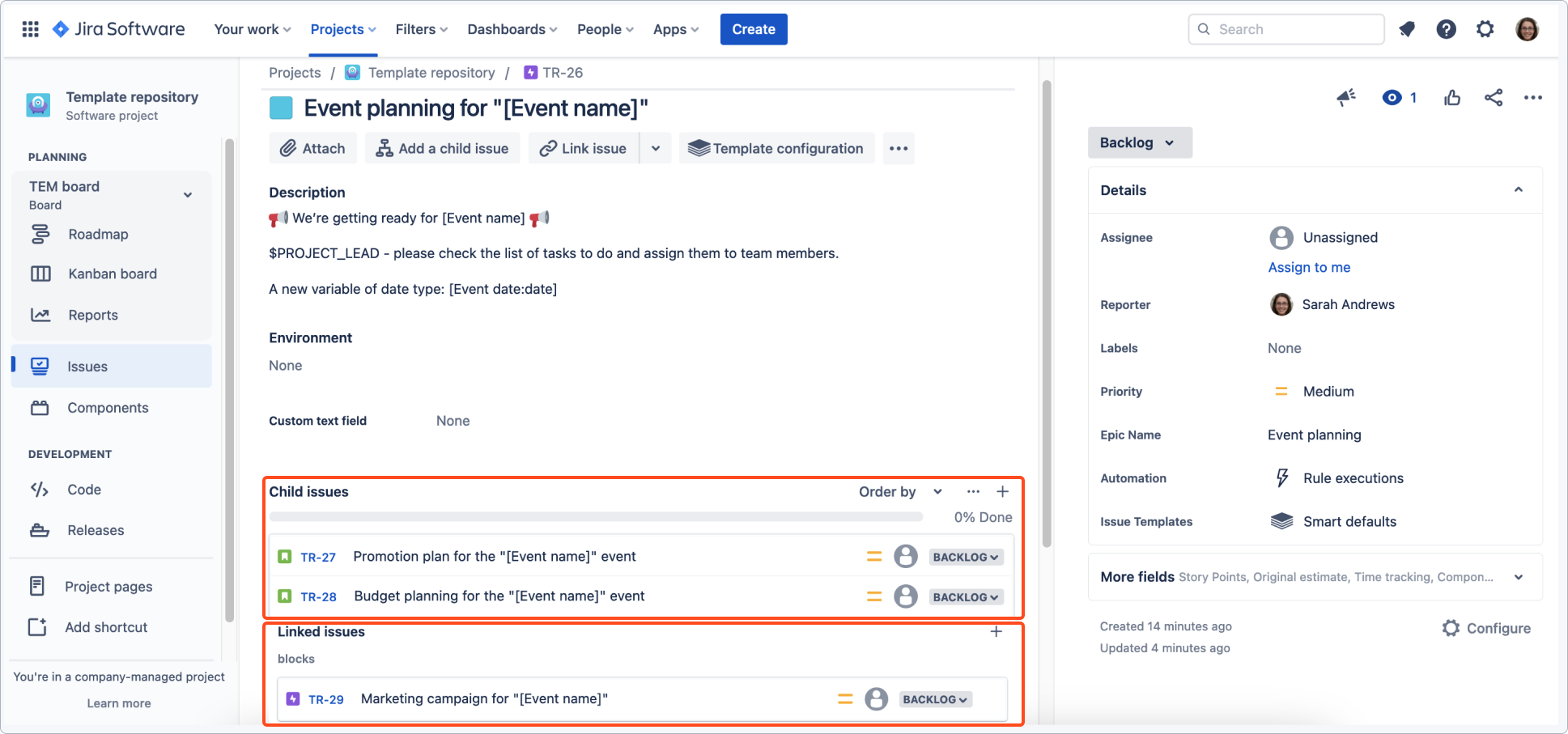
Child issues are configured using smart defaults to shift one week forward and copy components and the assignee from the parent.
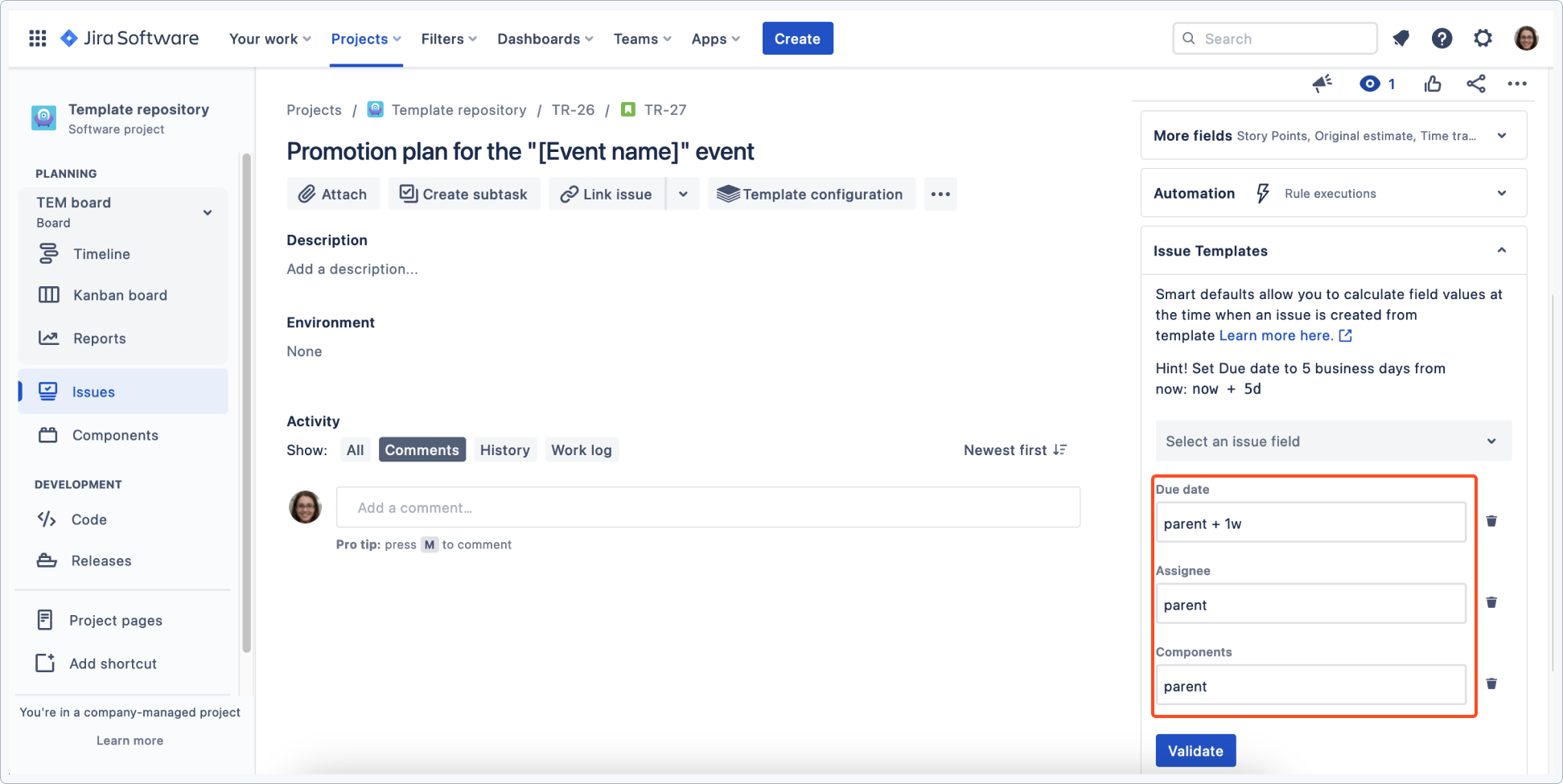
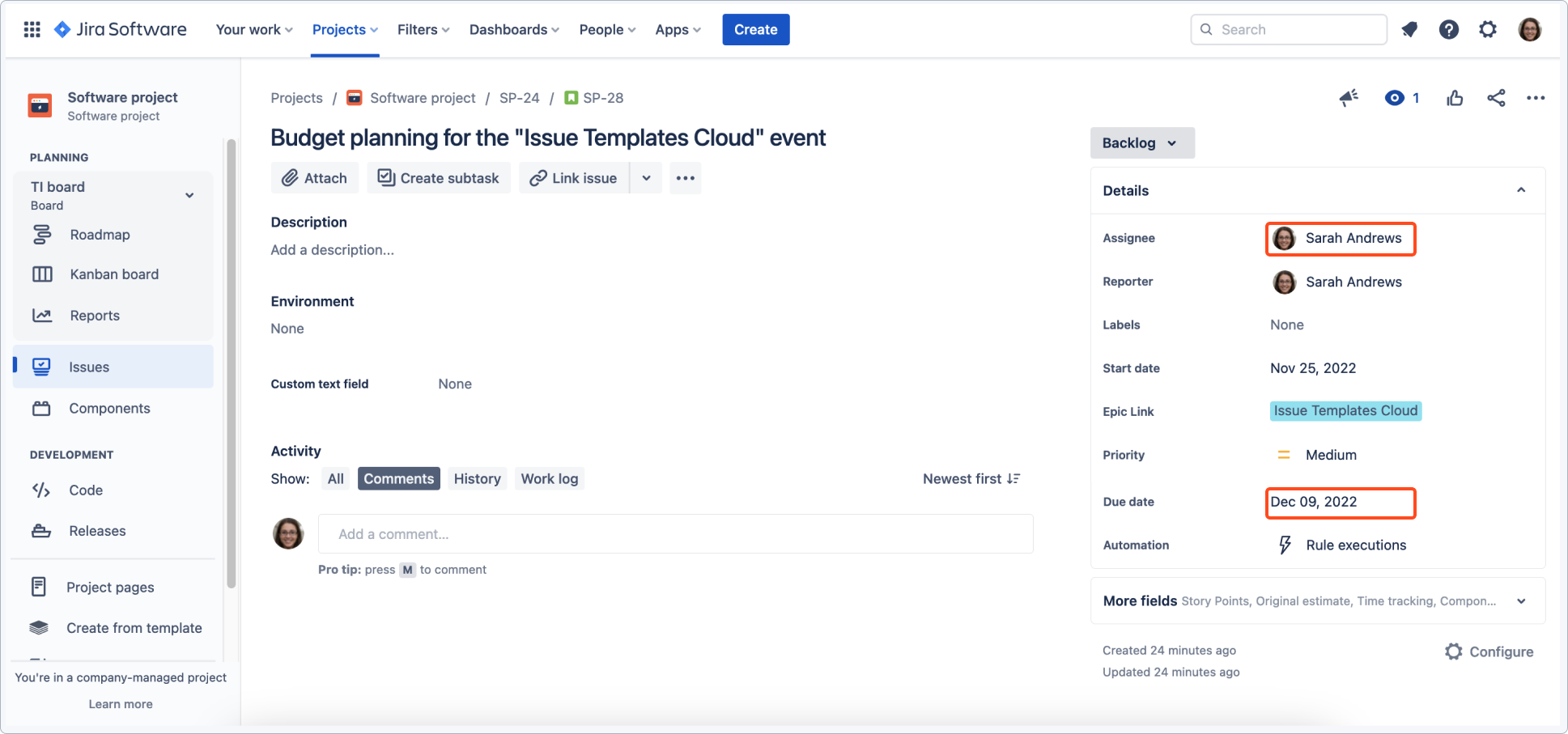
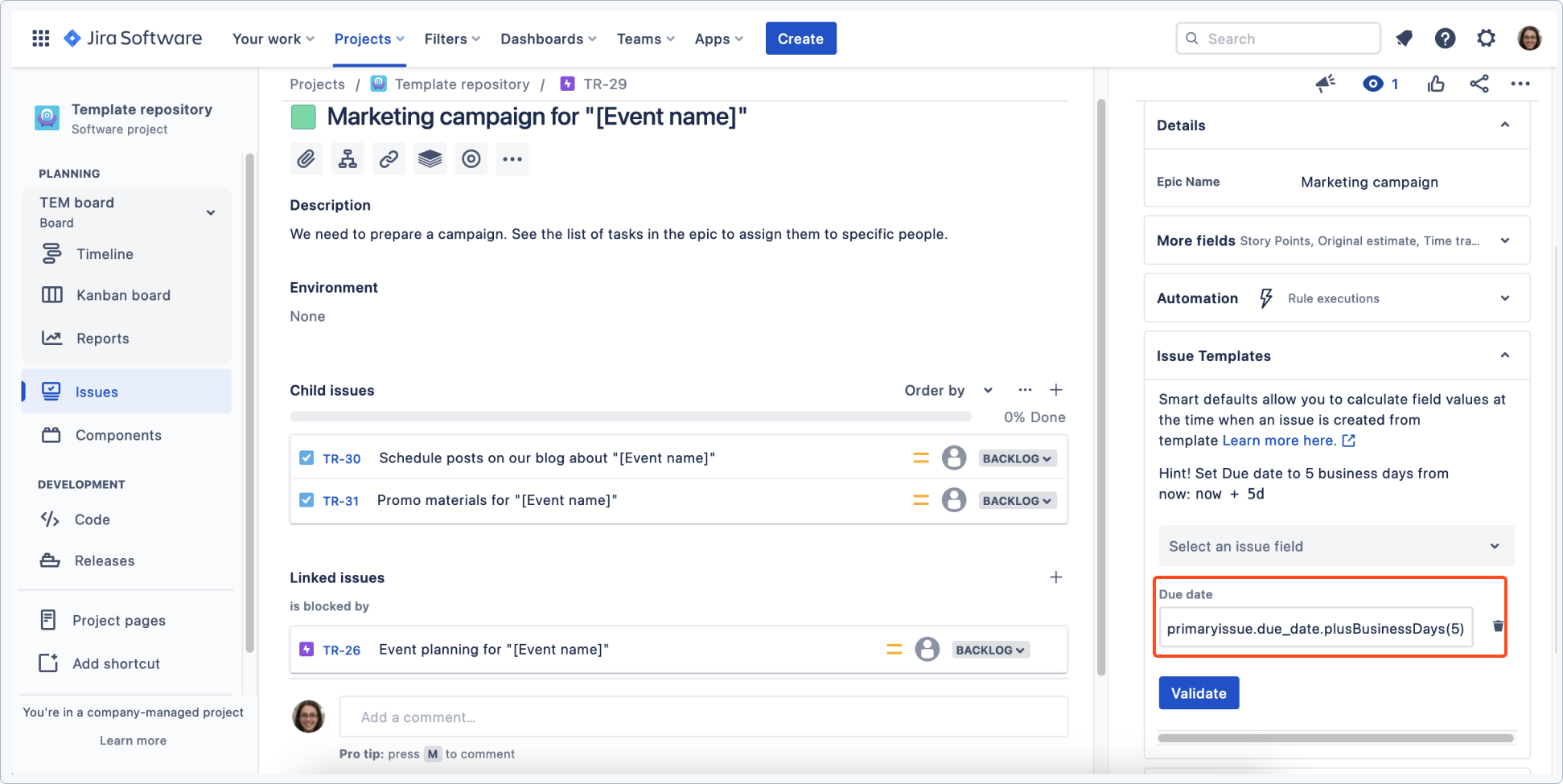
The linked epic is also configured to copy the due date from the main task and shift it in time.
Result
Both epics have been created and child issues with set values have been applied.
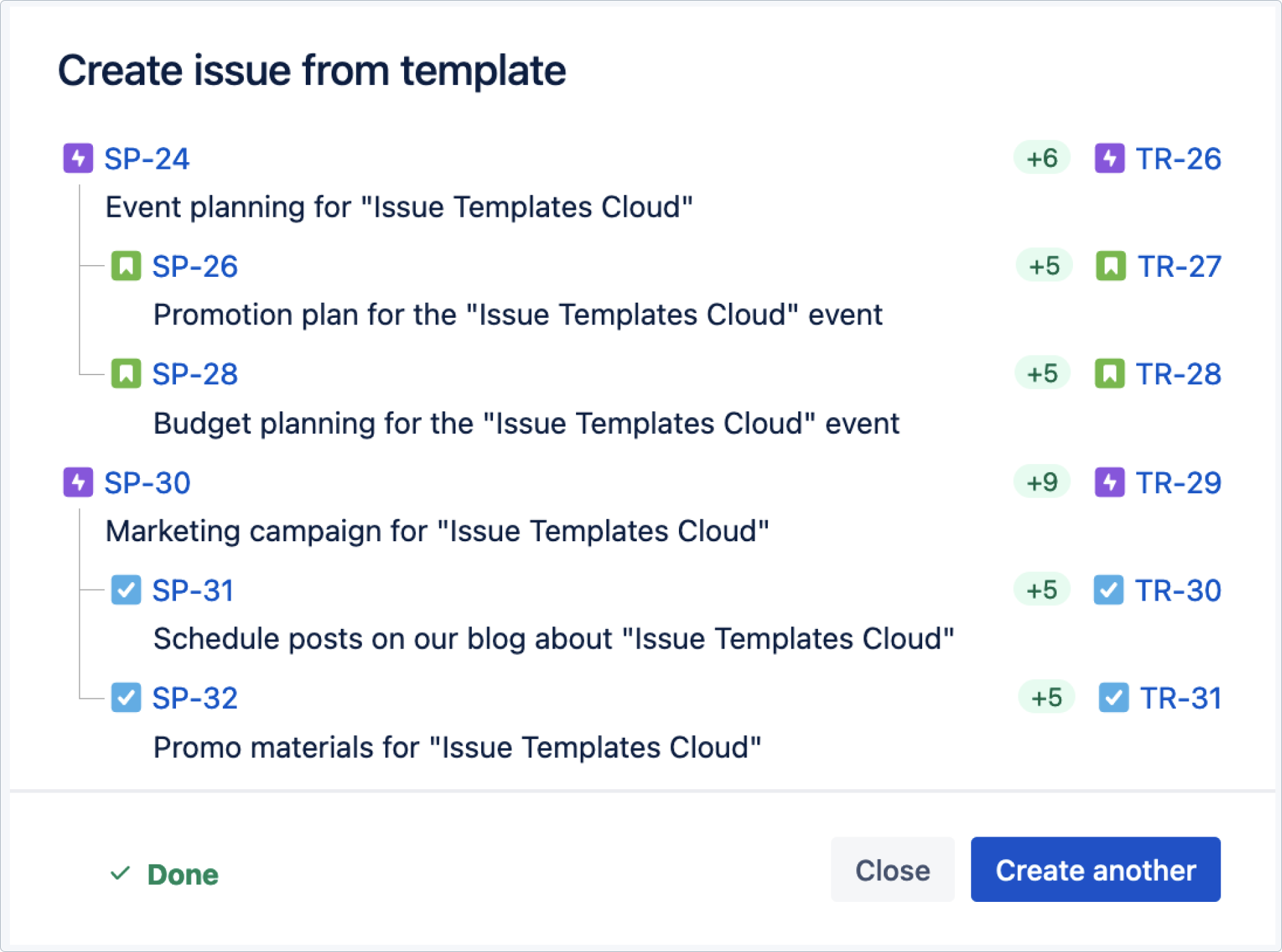
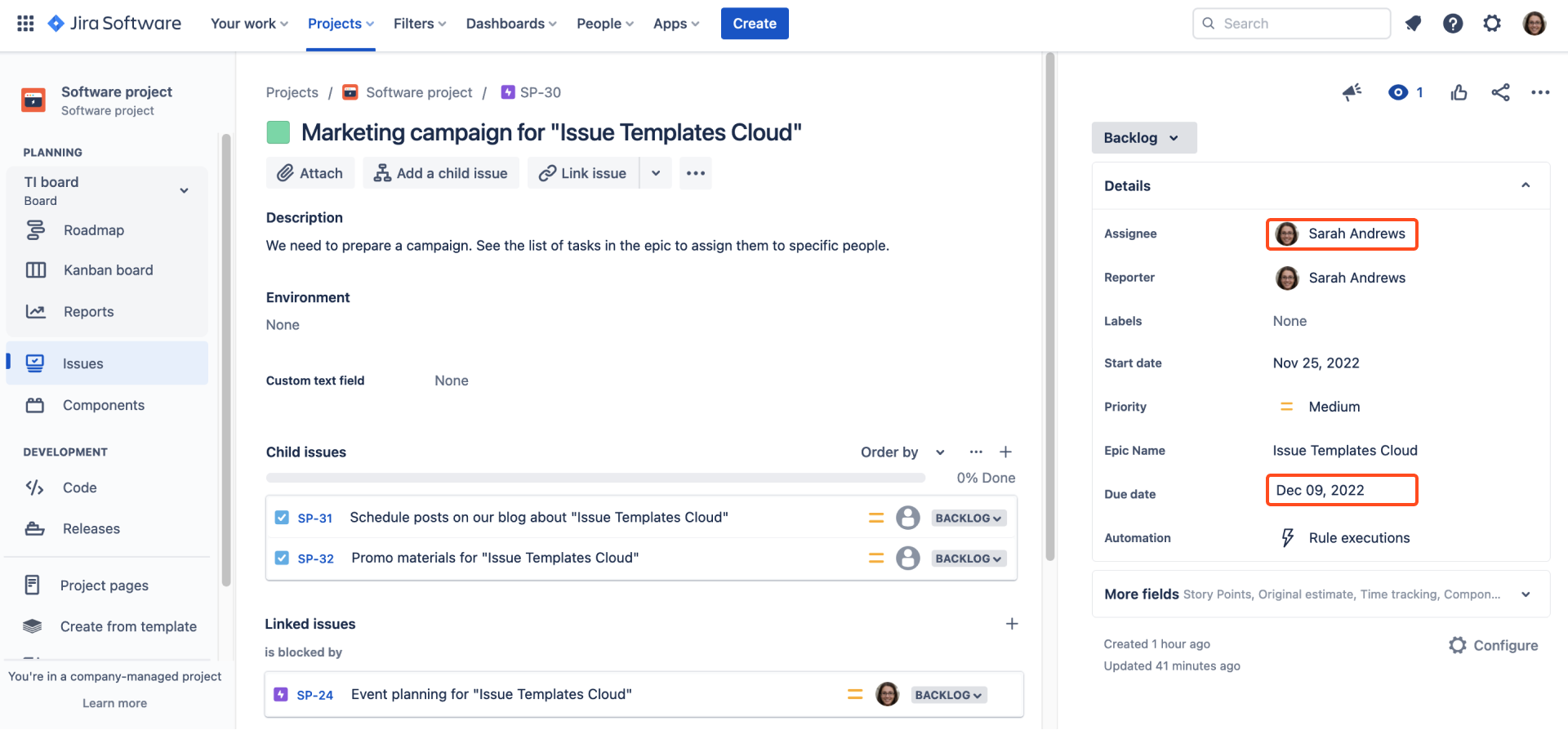
Child issues copied the assignee, components, and shifted the date as configured.
Due date of the linked epic has also been shifted.
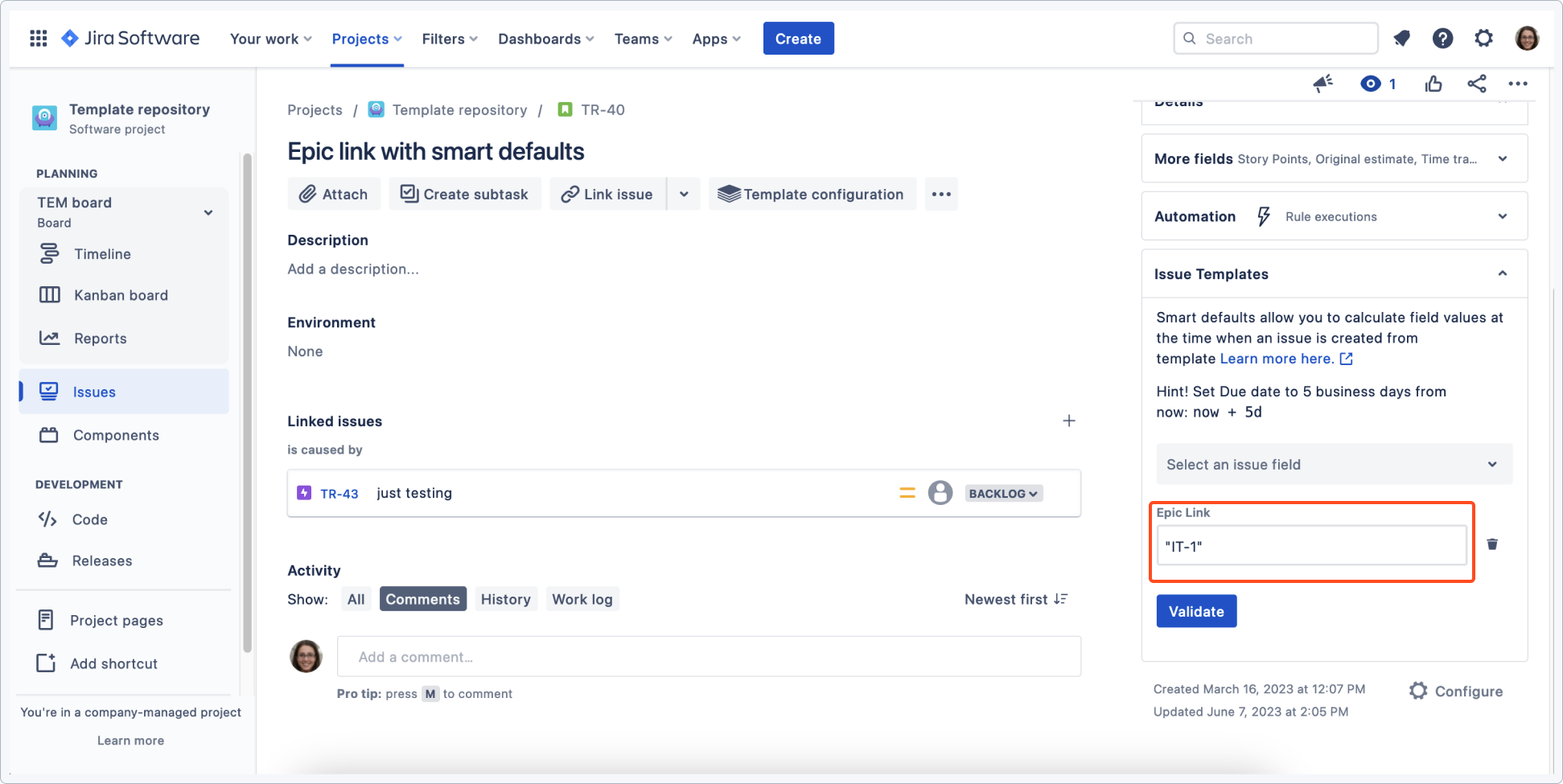
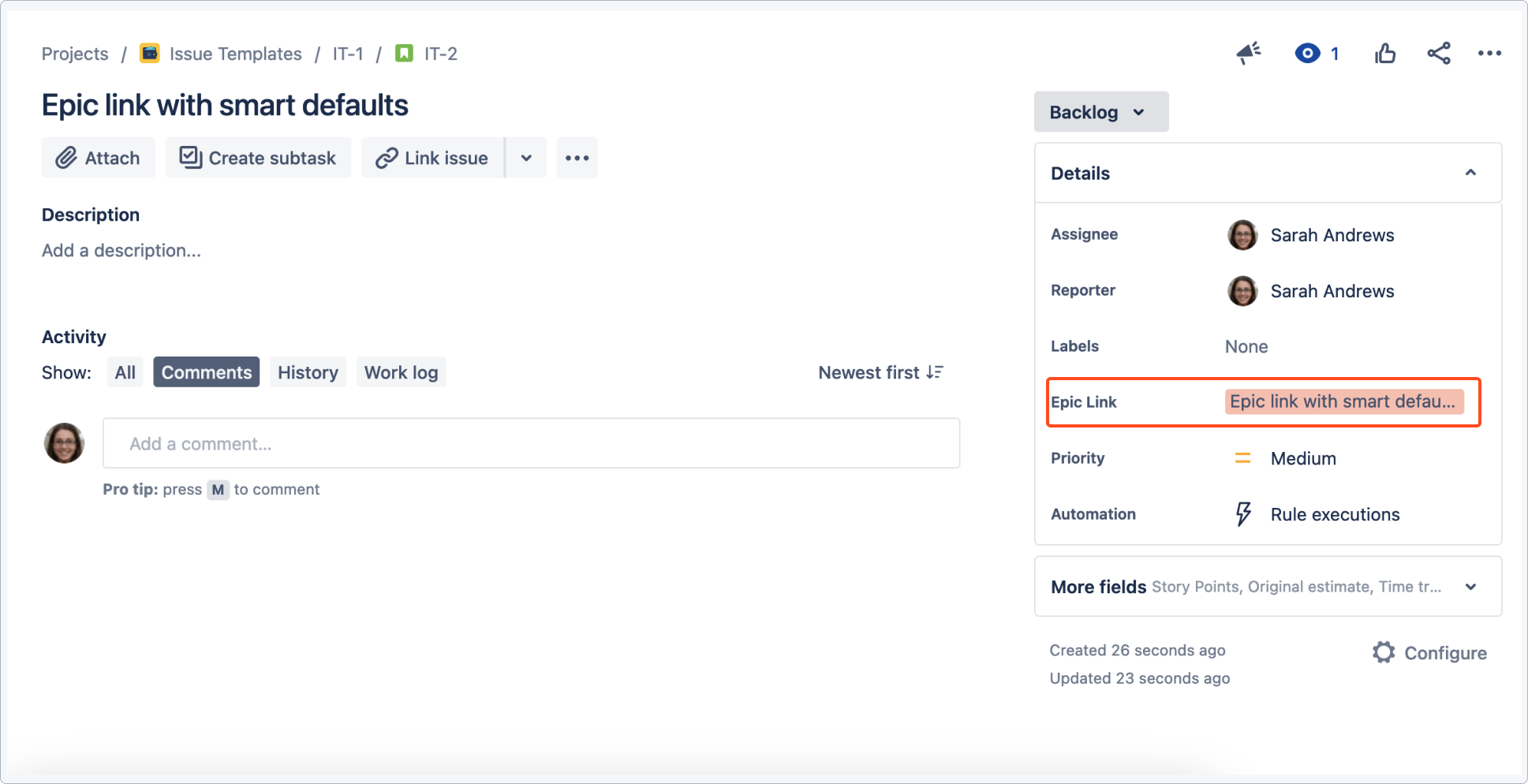
Use case 3 - Linking an epic with smart defaults
You can configure an epic link in smart defaults so that it will link to an already-existing epic. This way templates will automatically link to the specified epic in this project or another.